2a02:6ea0:d158:0000:0000:0000:01ba:253c, the internet, as we recognize it, has grown exponentially over time, which is most critical to improving a more significant current generation to cope with the developing range of gadgets and customers. 2a02:6ea0:d158:0000:0000:0000:01ba:253c, One of the most essential traits in recent times has been the transition from IPv4 (Internet Protocol model 4) to IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6). IPv6 addresses, like 2a02:6ea0:d158:0000:0000:0000:01ba:253c, constitute the destiny of the internet’s infrastructure, offering progressed capability, protection, and scalability.
In this newsletter, we’ll learn about the importance of IPv6, why it has become so advanced, how it differs from IPv4, and what makes addresses like 2a02:6ea0:d158:0000:0000:0000:01ba:253c a crucial part of the net’s destiny. We can also delve into the traumatic situations of the IPv6 transition, its role in IoT, and how it allows future net growth.
Understanding Internet Protocols
What is an Internet Protocol (IP)?
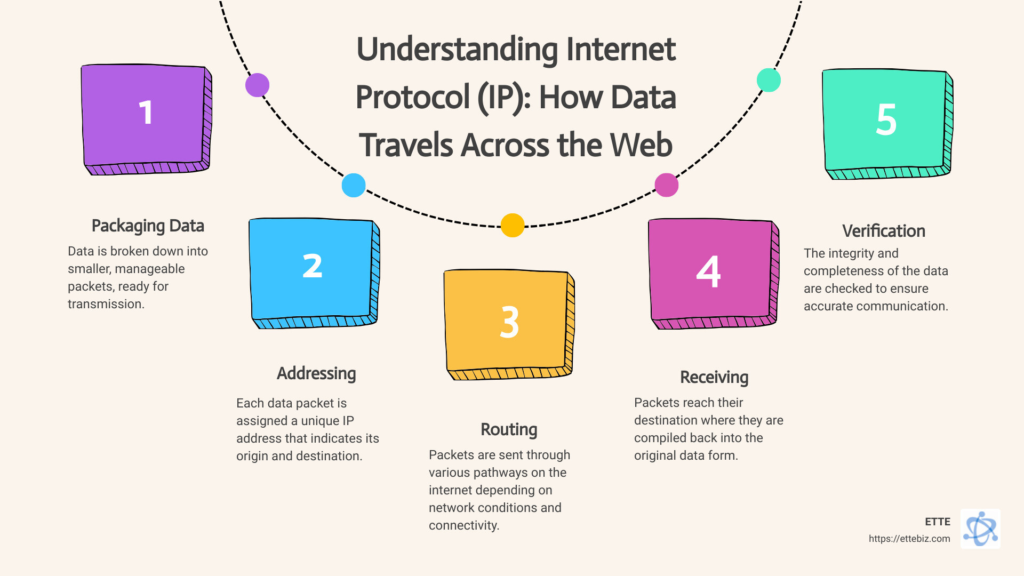
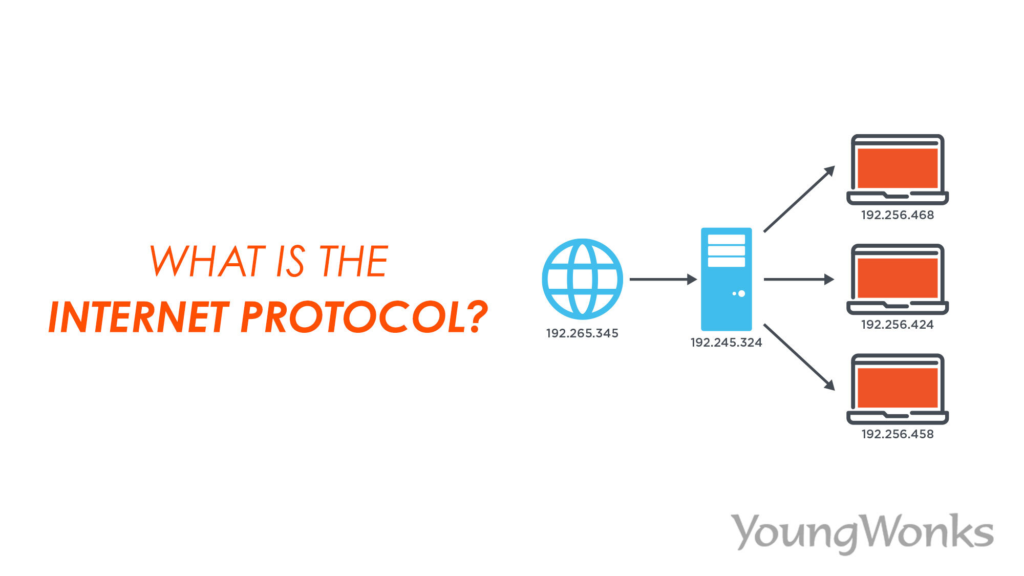
The net operates through the communique of several gadgets, such as IP addresses, which act as unique identifiers for each tool related to the net. This gadget lets in gadgets to deliver and gain records. There are number one versions of IP presently in use: IPv4 and IPv6.
The Role of IP Addresses
Every tool related to the net desires an IP address. These addresses allow for routing network information packets sooner or later from one tool to 3 different, ensuring the proper recipient receives the data. The shape of an IP deal is crucial to preserving a prepared and functioning internet.
IPv4 vs. IPv6
IPv4 has become the number one widely used version of the net protocol, presenting a 32-bit cope with a layout that can support more significant or a good deal less than 4—three billion precise addresses. As the kind of net-associated gadgets grew, it has become glaring that the pool of to-be-had IPv4 addresses may also want to be exhausted quickly. This shortage brought about the advent of IPv6, which uses a 128-bit address layout, vastly growing the to-be-had amount of particular addresses.
The Rise of IPv6
Why the Shift to IPv6?
The shift to IPv6 became critical because IPv4 was limited in coping with the vicinity. With the exponential boom of the net, driven by smartphones, laptop systems, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices, IPv4 is sufficient to cope with the increasing number of clients and gadgets.
The Benefits of IPv6
IPv6 was designed to address IPv4’s shortcomings. Its large coping area allows trillions of specific addresses, so we will avoid facing a coping scarcity in the foreseeable future. Additionally, IPv6 includes talents incorporating simplified header formats, advanced protection via compulsory helpful resources for IPSec, and better help for mobile devices and IoT.
Exploring Address2a02:6ea0:d158:0000:0000:0000:01ba:253c
IPv6 addresses, like 2a02:6ea0:d158:0000:0000:0000:01ba:253c, have a look at a hexadecimal layout and are composed of eight groups of four hexadecimal digits. 2a02:6ea0:d158:0000:0000:0000:01ba:253c, Each employer is separated through colons, making the addresses much longer than IPv4 addresses. This form permits the creation of nearly limitless shapes of unique addresses.
Differences Between IPv4 and IPv6
Address Space
The maximum apparent distinction between IPv4 and IPv6 is the shape of viable addresses. While IPv4 uses a 32-bit addressing tool, it is restricted to approximately four. Three billion addresses, IPv6’s 128-bit addressing device allows for an astronomical variety of addresses (spherical 340 undecillion). This solves the hassle of dealing with exhaustion that IPv4 confronted.
Simplified Routing
IPv6 simplifies routing by eliminating the need for Network Address Translation (NAT), a generation utilized in IPv4 to allow a couple of devices to percentage an unmarried public IP deal with. With IPv6, each tool will have its unique public IP, increasing network manipulation and lowering the load on routers.
Security Improvements
One of the critical upgrades in IPv6 includes help for IPSec, which is miles non-obligatory in IPv4. IPSec offers stop-to-give-up encryption and authentication, making IPv6 inherently more regular. This characteristic ensures information integrity, confidentiality, and authentication, which has been critical recently and is an increasing number of globally associated issues.
The Transition from IPv4 to IPv6
The Challenge of Transition
Despite the easy blessings of IPv6, the transition from IPv4 has been slow. This is because IPv4 has been used for many years, and many corporations depend closely on IPv4 infrastructure. Switching to IPv6 calls for enhancements to each hardware and software software software software, making it a steeply-priced and time-ingesting method.
Dual-Stack Approach
Many networks use a twin-stack approach to ease the transition, wherein every IPv4 and IPv6 is carried out concurrently. This allows devices to talk over each protocol, imparting backward compatibility with IPv4 at the identical time as often adopting IPv6.
Challenges Faced During Transition
Adopting IPv6 has faced several challenges, such as the cost of upgrading infrastructure, lack of IPv6 knowledge and expertise, and compatibility troubles with older software programs and hardware. However, as more gadgets and networks are being transferred to IPv6, the annoying situations are regularly addressed.
The Role of IPv6 in IoT
IPv6 and the Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) is one of the driving forces behind adopting IPv6. IoT refers to the network of physical devices connected to the net, with clever home gadgets, sensors, and business machines. Each of those gadgets requires a unique IP deal, making IPv6 important for the future of IoT.
Scalability for Billions of Devices
IPv6’s full-size address region makes it first-class for IoT, as it may accommodate billions of devices, every with its private unique IP address. This scalability is vital because the form of IoT devices continues to amplify exponentially.
Improved Network Efficiency
IPv6 improves the overall performance of the IoT network by permitting extra honest communication among gadgets. With its simplified header format and higher assistance for cell networks, IPv6 allows quicker statistics transmission and reduced latency, making it first-rate for IoT packages.
Security in IPv6 Networks
Built-in Security Features
One of the most suitable sized advantages of IPv6 is its advanced protection competencies. While IPv4 requires more excellent configuration for protection, IPv6 has IPSec built into the protocol, providing stop-to-surrender encryption and authentication with the aid of default.
Protecting Devices from Cyber Threats
Cybersecurity is a developing hassle with the development of massive kinds of devices related to the internet. IPv6’s protection features assist in protecting gadgets from cyber threats, such as information breaches, hacking attempts, and DDoS attacks. Clients can enjoy a more robust net revel by ensuring that each information transmitted over IPv6 networks is encrypted.
Challenges to IPv6 Security
Despite its blanketed protection skills, IPv6 isn’t always proof in opposition to protection worrying situations. Misconfigurations, statistics loss, and wrong implementation can cause vulnerabilities in IPv6 networks. Network administrators want to ensure proper protection functions are in place to leverage IPv6’s competencies.
IPv6 and the Future of the Internet
IPv6 as a Foundation for Future Growth
As the internet continues to conform, IPv6 will play a vital role in its growth. With the increasing variety of connected gadgets and emerging new technologies combined with 5G, IPv6’s scalability and overall performance may be necessary to keep a functioning internet.
The Importance of IPv6 for Developing Countries
IPv6 furthermore offers an opportunity for developing worldwide locations to leapfrog previous technology and bring together contemporary-day net infrastructures. By adopting IPv6, those international locations can bypass the constraints of IPv4 and create networks capable of assisting destiny upgrades.
Future Trends in IPv6 Adoption
While IPv6 adoption has been sluggish, it is progressively growing as more significant corporations and internet issuer businesses make the transfer. In the imminent years, we can look at the enormous adoption of IPv6, pushed by the resource of way of the growing name for internet-linked gadgets and the want for better protection and community essential overall performance.
The Road Ahead: Full IPv6 Deployment
Steps to Achieve Full IPv6 Deployment
The entire IPv6 deployment should require a coordinated effort from governments, organizations, and internet service carriers. Governments can play a characteristic with the valuable beneficial aid of enforcing pointers that inspire IPv6 adoption. At the same time, organizations and ISPs need to spend money on upgrading their infrastructure to assist the brand-new protocol.
Ongoing Challenges
Despite the improvements, several disturbing conditions remain on the street to complete the IPv6 deployment. These include upgrading legacy structures, losing IPv6 records, and compatibility troubles with older devices and packages. Overcoming the annoying situations requires persistent funding and training.
The Future of Internet Protocols
As we appear to the future of the internet, IPv6 represents a crucial breakthrough in growing a more scalable, consistent, and inexperienced worldwide community. By embracing IPv6, we can ensure that the net amplifies and evolves, assisting new technology and upgrades for destiny years.
FAQ’S
What is the significance of IPv6 addresses like 2a02:6ea0:d158:0000:0000:0000:01ba:253c?
IPv6 addresses, consisting of 2a02:6ea0:d158:0000:0000:0000:01ba:253c, represent the following generation of net addressing. These addresses provide a full-size variety of particular IPs, solving the issue of address exhaustion that plagued IPv4. The large address space helps trillions of unique IP addresses, making sure that every tool, which includes destiny technology like IoT, may be uniquely diagnosed and related to the internet.
How does IPv6 improve safety compared to IPv4?
IPv6 has built-in safety capabilities like IPSec, which gives end-to-stop encryption and authentication, making it more secure than IPv4, in which IPSec is optionally available. This integrated safety characteristic facilitates protecting statistics integrity and confidentiality, reducing the risks of cyber threats including hacking, statistics breaches, and DDoS attacks.
Why has the transition from IPv4 to IPv6 been sluggish, and what challenges are worried about?
The transition from IPv4 to IPv6 has been sluggish due to the fee and complexity of upgrading infrastructure, compatibility issues with older hardware and software, and the enormous reliance on present IPv4 systems. Many businesses still use a dual-stack approach to guide both IPv4 and IPv6, permitting a smoother transition even as keeping off immediate disruptions in providers.
Conclusion
IPv6 is not the best preference for addressing the exhaustion trouble of IPv4; it’s miles a transformative technology that paves the way for the destiny of the net. The introduction of IPv6 addresses like 2a02:6ea0:d158:0000:0000:0000:01ba:253c demonstrates the protocol’s ability to revolutionize how gadgets talk, beautify safety, and guide the ever-developing Internet of Things (IoT). Despite the traumatic conditions of transitioning from IPv4, the blessings of IPv6, on scalability, simplified routing, and protection, make it a crucial issue for the future of internet increase. As IPv6 adoption grows, it’ll release new possibilities for innovation and connectivity across the globe.